**"The Role Of Coil Galvanizing Lines In Corrosion Resistance And Metal Durability"**
Certainly! Here's a compelling introduction for your article titled **"The Role of Coil Galvanizing Lines in Corrosion Resistance and Metal Durability"**:
---
In today’s industrial landscape, the longevity and reliability of metal products are more critical than ever. Corrosion can compromise structural integrity, leading to costly repairs and safety concerns. Enter coil galvanizing lines—a transformative technology that enhances metal surfaces with a protective zinc coating, dramatically improving corrosion resistance and extending metal durability. But how exactly do these lines work, and why are they vital in various manufacturing sectors? Dive into this article to discover the science behind coil galvanizing lines and their pivotal role in safeguarding metals against the harshest elements, ensuring your investments stand the test of time.
---
Would you like it to be more technical, more casual, or tailored to a specific audience?

- Understanding Coil Galvanizing Lines: An Overview
**Understanding Coil Galvanizing Lines: An Overview**
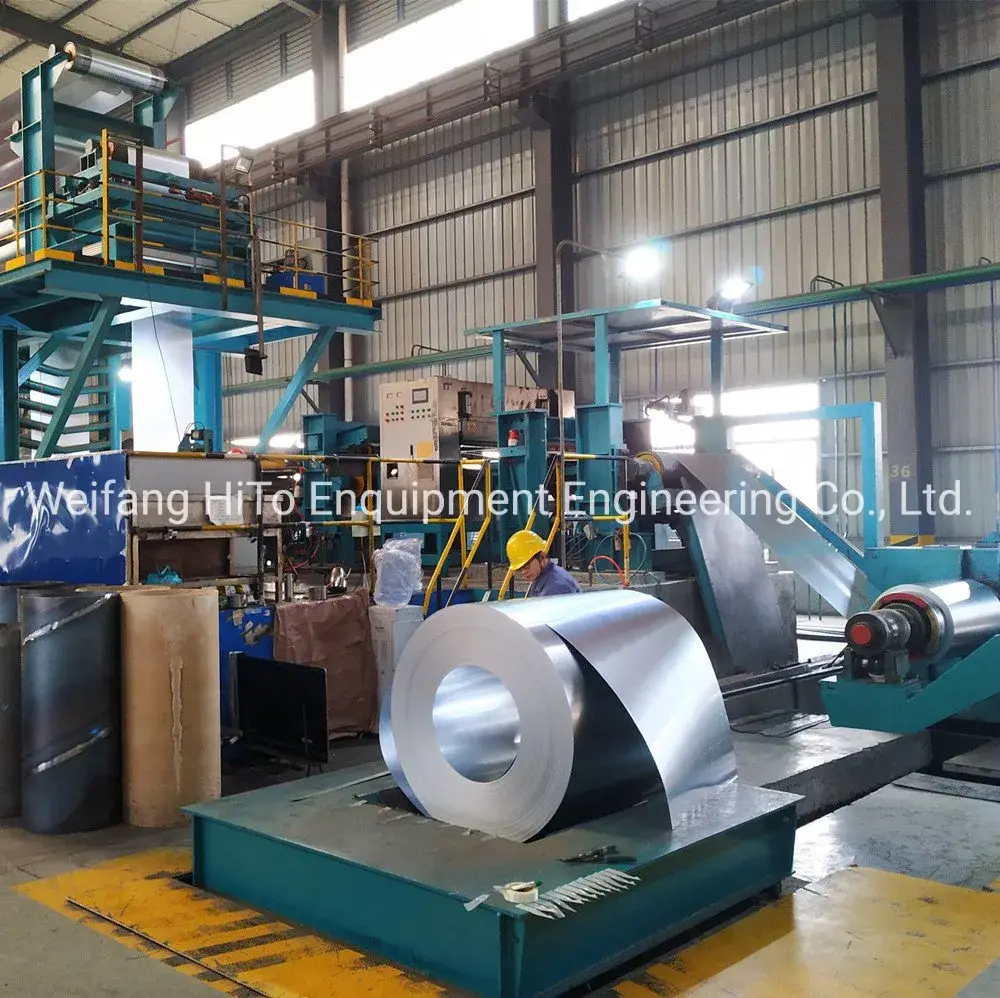
Coil galvanizing lines play a pivotal role in the metal processing industry, particularly in enhancing corrosion resistance and extending the durability of steel products. These specialized production lines are engineered to apply a protective zinc coating to steel coils, ensuring that the underlying metal is safeguarded against environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and air exposure, which typically cause rust and corrosion. As the demand for long-lasting, cost-effective metal materials rises across various industries—ranging from automotive and construction to appliances and infrastructure—the coil galvanizing line has become an indispensable asset.
At its core, a coil galvanizing line is a highly automated and continuous processing system designed to galvanize steel coils efficiently and uniformly. The process begins with the uncoiling of raw steel sheets, which are then subjected to rigorous cleaning and surface preparation stages. These preliminary steps are critical, as they remove oils, dirt, oxides, and other contaminants that could impair the adhesion of the zinc coating. Typically, cleaning involves chemical treatments such as acid pickling, degreasing, and rinsing, followed by drying to prepare the surface thoroughly.
Once cleaned, the steel coils proceed to the galvanizing section, where they are immersed in a molten zinc bath at temperatures generally around 450°C. This hot-dip galvanizing method ensures the formation of a metallurgical bond between the zinc and the steel substrate. As the coil passes through the zinc bath, a series of iron-zinc alloy layers form on the surface, providing a robust, adherent coating that cannot be easily peeled or scratched off. After exiting the bath, the coated coil moves through a cooling zone that solidifies the zinc, producing a smooth, shiny, and corrosion-resistant finish.
Modern coil galvanizing lines incorporate several sophisticated technologies to optimize coating quality, line speed, and operational efficiency. For instance, air knives are strategically positioned to control the thickness of the zinc layer by blowing off excess molten zinc from the steel surface before it solidifies. This precise control prevents over-coating, reducing material costs while maintaining protective performance standards. Additionally, coil galvanizing lines often integrate real-time monitoring systems and automation controls, enabling operators to adjust parameters such as bath temperature, line speed, and coating thickness dynamically, thereby maintaining strict process control and product consistency.
One of the key advantages of processing galvanized steel coils on a coil galvanizing line is the ability to produce large volumes of coated material continuously. This industrial-scale throughput reduces lead times and lowers production costs compared to batch galvanizing methods, making it highly attractive for high-demand sectors. Moreover, the coil form of zinc-coated steel is highly versatile, allowing manufacturers downstream to slit, cut, and form it into various final products tailored for specific applications.
From a material science perspective, the zinc coating applied via coil galvanizing lines significantly improves metal durability by creating a physical barrier and acting as a sacrificial anode. This dual mechanism prevents corrosion from penetrating and weakening the metal substrate. Furthermore, zinc’s ability to self-heal minor scratches through the formation of corrosion products confers additional longevity to galvanized steel—a major reason why coil galvanizing lines are indispensable in producing structural steel items that must withstand harsh outdoor environments.
Environmental and regulatory considerations have also influenced coil galvanizing line technology. Modern lines emphasize the closed-loop recycling of chemicals and zinc, waste minimization, and energy efficiency, aligning with increasingly stringent sustainability standards. Advances in coating chemistry and process controls have led to thinner yet highly effective zinc layers, reducing zinc consumption without compromising corrosion resistance.
In summary, the coil galvanizing line is a sophisticated and vital process in the steel manufacturing sector. By delivering consistently high-quality zinc coatings on steel coils, it directly contributes to the enhanced corrosion resistance and prolonged durability of metal products widely used across industries. Its combination of continuous processing, precise coating control, and integration with modern automation ensures that coil galvanizing lines remain at the forefront of metallurgical innovation and practical manufacturing solutions.
- How Coil Galvanizing Enhances Corrosion Resistance
**- How Coil Galvanizing Enhances Corrosion Resistance**
Coil galvanizing is a critical process in protecting steel materials from the relentless degradation caused by corrosion. Within the broader context of metal treatment and durability, the use of a coil galvanizing line plays a pivotal role in extending the life and performance of steel products. At its core, coil galvanizing involves a continuous hot-dip process wherein steel coils are coated with a thin yet highly effective layer of zinc. This zinc layer serves as a durable barrier that shields the metal underneath from environmental factors that typically cause corrosion, such as moisture, oxygen, and pollutants.
The coil galvanizing line is specially designed to optimize this process. Steel coils enter the galvanizing line and pass through a succession of stages – cleaning, fluxing, and immersion in a molten zinc bath – before cooling and being rewound into coils. This continuous operation ensures uniform coating thickness and strong adhesion of zinc to the base metal, which is crucial for long-term corrosion resistance. Any imperfection or uneven coating could harbor moisture or contaminants that accelerate rust formation. Therefore, the precision engineering of coil galvanizing lines enhances not only productivity but also the protective qualities of the galvanized steel.
One of the key mechanisms through which coil galvanizing improves corrosion resistance is through the sacrificial protection provided by zinc. Zinc is more electrochemically active than steel, meaning that if the galvanized coating gets scratched or compromised, the zinc will corrode preferentially, protecting the underlying steel from rusting. This galvanic protection ensures that even damaged areas maintain a degree of defense, which is especially valuable for structural and automotive steel where surface damage is possible during fabrication, transport, or use.
Furthermore, the metallurgical bonding formed during the hot-dip galvanizing process within the coil galvanizing line is not just a simple overlay. Instead, an alloy layer forms between the zinc and the steel, melding the two materials on a microstructural level. This metallurgical interlayer dramatically improves the abrasion resistance and hardness of the galvanized coating, making it less prone to flaking and wear that can expose steel to corrosive agents. The thickness and quality of this alloy layer are closely controlled by the precision process parameters automated in modern coil galvanizing lines, ensuring consistent corrosion protection across extensive production runs.
Another important factor that contributes to enhanced corrosion resistance through coil galvanizing lines is the capability for customization and control over coating specifications. Different applications demand varied levels of zinc coating thickness and post-treatment processes such as passivation or chromate conversion coatings. The coil galvanizing line can be adjusted to meet these requirements, producing galvanized steel with coatings tailored to withstand particular environmental conditions—whether it’s the high humidity of coastal regions, exposure to industrial pollutants, or long-term outdoor use under UV radiation. This flexibility not only boosts corrosion resistance but also optimizes material cost and performance based on specific end uses.
Additionally, coil galvanizing lines are often integrated with advanced monitoring and quality control systems. Sensors and automated inspection technologies track parameters such as coating weight, surface cleanliness, and bath chemistry in real time. These technologies ensure that the galvanized coating meets strict international standards like ASTM A653 or EN 10346, which define performance benchmarks for corrosion resistance. By utilizing a coil galvanizing line equipped with these advanced features, manufacturers guarantee a high level of reliability and durability in the galvanized products they produce.
In summary, the coil galvanizing line is indispensable in enhancing corrosion resistance by delivering a uniform, metallurgically bonded zinc coating that provides sacrificial protection, mechanical robustness, and adaptability to specific environmental conditions. Through precision engineering, continuous operation, and integrated quality control, coil galvanizing lines transform ordinary steel coils into corrosion-resistant, long-lasting materials suited for diverse applications from construction to automotive to appliance manufacturing.
- The Impact of Galvanizing on Metal Durability and Lifespan
**The Impact of Galvanizing on Metal Durability and Lifespan**
In the realm of metal preservation and protection, galvanizing has emerged as a cornerstone technique, significantly enhancing the durability and lifespan of metal components. Particularly, the use of coil galvanizing lines—highly specialized production setups designed to apply zinc coatings on metal coils—has revolutionized how industries approach corrosion resistance and structural longevity. This article explores the profound impact galvanizing, facilitated by coil galvanizing lines, has on the durability and lifespan of metal, with an emphasis on underlying mechanisms and practical benefits.
At its core, galvanizing is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rust formation. The zinc serves as a physical and chemical shield, insulating the base metal from corrosive elements such as moisture, oxygen, and industrial pollutants. Unlike simple surface painting or coating, galvanizing creates a metallurgically bonded layer that adheres seamlessly to the metal substrate, ensuring long-term protection. When galvanizing is conducted on coils via coil galvanizing lines, the process achieves remarkable uniformity and consistency, which directly correlates to enhanced performance outcomes.
**Protection Mechanisms Enhancing Durability**
The zinc coating applied through coil galvanizing lines primarily protects metal through two mechanisms: barrier protection and cathodic protection. As a barrier, the zinc layer physically isolates the iron or steel from environmental exposure, preventing water and air from initiating the oxidation process that leads to rust. Moreover, if the zinc coating incurs minor breaches or damages, it offers cathodic protection—acting as a sacrificial anode. Because zinc is more electrochemically active than iron, it corrodes preferentially, protecting the underlying metal from corrosion even when the barrier is compromised. This dual protection strategy built into the galvanizing process significantly extends the functional lifespan of metals in harsh environments.
**Impact on Metal Durability**
The use of coil galvanizing lines elevates metal durability by ensuring consistent, high-quality zinc coatings across entire metal coils. The automation and precision control inherent to coil galvanizing lines allow for tight regulation of coating thickness, temperature, and immersion time during the galvanizing process. These factors critically influence the adherence strength and uniformity of the zinc protective layer, which directly affects durability. Metals coated on modern coil galvanizing lines show superior resistance to environmental wear, less susceptibility to surface damage caused by mechanical stress, and improved resistance to chemical attack.
Additionally, the galvanizing process enhances metal strength by reducing the formation of micro-cracks and other surface imperfections that could act as stress concentrators or corrosion initiation sites. Coil galvanizing lines, therefore, don’t just apply a protective coating—they contribute to creating a more robust and resilient metal substrate capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to demanding conditions.
**Extending Lifespan in Various Applications**
The extension of metal lifespan due to galvanizing on coil galvanizing lines is evident across multiple industrial applications, from construction and automotive manufacturing to electrical appliances and infrastructure. For example, galvanized steel structures such as bridges, transmission towers, or outdoor panels demonstrate lifespans that can exceed 50 years without requiring major maintenance or replacement. This is a direct result of the consistent and effective zinc protection that coil galvanizing lines provide, which safeguards metals against accelerated aging caused by weather, moisture, and pollution.
In sectors like automotive manufacturing, coil galvanized steel parts are less prone to rust and degradation, improving vehicle longevity and reducing repair costs. Similarly, coil galvanizing lines enable the rapid production of galvanized metal, making the process economically viable for large-scale deployment, and consequently, more industries can benefit from enhanced metal durability.
**Environmental and Economic Implications**
Beyond durability, galvanizing through coil galvanizing lines offers environmental advantages by reducing the frequency of metal replacement and maintenance. Longer-lasting metal components translate to less resource consumption and lower carbon footprints over the product lifecycle. Economically, the upfront investment in coil galvanizing lines pays off through decreased downtime and maintenance expenses, supporting sustainable industrial practices.
In conclusion, the impact of galvanizing on metal durability and lifespan cannot be overstated. Coil galvanizing lines, as sophisticated and efficient manufacturing platforms, ensure that this protective process is applied with precision and consistency. The resulting zinc coatings not only safeguard metals from corrosion but also contribute to stronger, longer-lasting components that withstand the stresses of both natural and industrial environments. This synergy between advanced galvanizing technology and metal performance represents a critical advancement in materials engineering, promising more durable infrastructure and products for the future.
- Technological Advances in Coil Galvanizing Processes
**- Technological Advances in Coil Galvanizing Processes**
The coil galvanizing line has undergone significant technological advancements over recent decades, profoundly transforming the coil galvanizing process to enhance corrosion resistance and metal durability. As industries increasingly demand higher-performing metal products, improvements in coil galvanizing technologies have become critical to meeting these expectations. The evolution of coil galvanizing lines has focused primarily on refining process efficiency, improving coating uniformity, enhancing environmental sustainability, and enabling customization to satisfy diverse application requirements.
Traditionally, coil galvanizing involved dipping steel coils into molten zinc baths to form a protective metallic coating. While the foundational method remains, innovations in both equipment and process control have pushed the boundaries of what coil galvanizing lines can achieve. Modern coil galvanizing lines now integrate advanced automation systems empowered by sensors and real-time feedback controls. These innovations allow precise regulation of line speed, bath temperature, and dross removal, ensuring consistent coating thickness along with superior adhesion of the zinc layer to the steel substrate.
One of the most notable technological advances is the adoption of continuous online monitoring systems. These systems employ optical sensors, X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and ultrasonic thickness gauges directly within the coil galvanizing line to measure the coating’s quality instantaneously. The data collected is processed through sophisticated algorithms that immediately adjust process parameters to maintain strict compliance with product specifications. This closed-loop control minimizes material waste and reprocessing, significantly reducing production costs—and crucially, it enhances the corrosion resistance characteristics by delivering an optimally uniform zinc coat.
Another critical innovation in coil galvanizing lines is the development of new alloy coatings beyond traditional pure zinc. Alloy baths, such as zinc-aluminum or zinc-nickel mixtures, have been incorporated due to their superior protective qualities and improved mechanical properties. Modern coil galvanizing lines are equipped to handle the precise temperature and chemical composition requirements needed to consistently apply these advanced coatings. For example, zinc-aluminum alloy coatings demonstrate enhanced resistance to white rust and better wear resistance, making them favorable for automotive and construction steels exposed to harsh environments.
Furthermore, modern coil galvanizing lines emphasize sustainability through more environmentally friendly processes. Innovations include closed-loop zinc recovery systems that recycle excess zinc from the bath, reducing raw material consumption and environmental discharge. Additionally, the use of advanced gas burners with improved energy efficiency and lower emissions has been integrated downstream of the galvanizing bath. Some processes now incorporate inline pre-treatment techniques that reduce or eliminate hazardous chemicals traditionally used in surface cleaning before galvanizing, further minimizing the environmental footprint of coil galvanizing operations.
Surface engineering technologies have also evolved hand-in-hand with coil galvanizing lines. Pre-treatment processes, such as ultra-pure chemical cleaning and passivation, improve coating adhesion and enhance the longevity of the galvanized layer. Post-treatment innovations, including the application of thin organic passivation films or advanced chromate-free coatings, are increasingly integrated into coil galvanizing lines. These treatments not only improve initial corrosion resistance but also bolster the performance of coated steel in prolonged outdoor conditions without sacrificing recyclability.
Automation and digitalization also play an indispensable role in the current generation of coil galvanizing lines. Industry 4.0 concepts are being introduced, linking galvanizing lines to integrated manufacturing execution systems (MES) and digital twins that simulate process changes and forecast maintenance needs. Predictive maintenance driven by artificial intelligence (AI) helps avert unscheduled downtime and extends the operational lifespan of coating lines, which directly contributes to continuous high-quality output and reliability in galvanizing performance.
Lastly, the modular construction of modern coil galvanizing lines offers unparalleled flexibility in adapting to changing market demands. Line configurations can now be customized to handle diverse alloy combinations, varying coil widths and thicknesses, and specialized coating weights with minimal downtime. This flexibility supports rapid transitions between product types—from highly corrosion-resistant automotive-grade coils to building industry materials designed for aesthetic galvanized finishes—without compromising process effectiveness.
In conclusion, technological advances in coil galvanizing processes have revolutionized coil galvanizing lines into sophisticated, efficient, and environmentally conscious manufacturing platforms. By combining real-time process controls, alloy innovations, digital integration, and sustainable practices, coil galvanizing lines now serve as pivotal systems for producing metal products that meet the highest standards of corrosion resistance and durability. These advancements continue to broaden the applications and improve the performance of galvanized steel products across numerous industrial sectors.
- Applications and Benefits of Galvanized Metals in Industry
**Applications and Benefits of Galvanized Metals in Industry**
The use of galvanized metals has become a cornerstone in various industrial sectors, largely driven by their superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability. Central to the production of galvanized metals is the coil galvanizing line, a highly efficient and automated system designed to apply a protective zinc coating to metal coils. This process plays a critical role in extending the lifespan of metals used in construction, automotive, electrical, and many other industries, providing both economic and functional advantages.
One of the primary applications of galvanized metals is in the construction industry, where they are widely used for structural steel, roofing, wall panels, and rebar. The coil galvanizing line ensures the steel coils are uniformly coated with a layer of zinc, which serves as a sacrificial barrier protecting the base metal from atmospheric corrosion, especially in harsh environments. This corrosion resistance significantly reduces maintenance costs and improves the longevity of buildings and infrastructure. For example, galvanized steel components in bridges, industrial plants, and residential buildings can resist rusting for several decades, even when exposed to extreme weather conditions such as rain, snow, and humidity.
In the automotive industry, galvanized metals are extensively used for body panels, frames, and chassis components. The coil galvanizing line offers high throughput and consistent coating thickness, which guarantees reliability in performance for these applications. Zinc coating protects the metal parts from rust caused by exposure to road salts, moisture, and mechanical wear. This corrosion resistance not only improves vehicle safety but also enhances the resale value of cars by reducing structural degradation. Additionally, because the coil galvanizing process can be integrated with other metal treatment steps, manufacturers benefit from a streamlined production cycle, reducing lead times and improving cost efficiency.
Electrical and electronics industries also benefit from galvanized metals. Electrical enclosures, cable trays, and grounding systems often utilize galvanized steel to ensure protection against electrical faults caused by corrosion damage. The coil galvanizing line allows the production of thin-gauge galvanized sheets that are then formed into precision components. This versatility is valuable in producing parts that require both corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Moreover, the zinc coating can act as a barrier to oxidation, preventing failure in critical electrical connections and equipment enclosures.
Agricultural and outdoor equipment manufacturing is another sector that depends heavily on galvanized metals. Items such as fencing, irrigation pipes, storage tanks, and machinery are routinely exposed to moisture and chemicals that accelerate metal degradation. The coil galvanizing line enables producers to manufacture galvanized steel at scale, providing robust protective coatings that significantly lengthen the service life of these products. This durability translates into less frequent replacement and thus lower cost of ownership for farmers and outdoor equipment operators.
Beyond these applications, galvanized metals offer environmental advantages related to sustainability. Because zinc coating extends the lifespan of materials, fewer resources are consumed over time to replace corroded parts. Moreover, the zinc used in galvanizing is recyclable, and steel itself is highly recyclable, contributing to circular economy initiatives. The coil galvanizing line, with its precision controls and efficient use of materials, minimizes waste and ensures that zinc application is optimized, reducing environmental impact during production.
From an economic perspective, galvanized metals produced by coil galvanizing lines deliver significant benefits. The upfront investment in galvanized steel may be slightly higher than untreated steel, but the reduction in maintenance, repair, and downtime costs quickly offsets the initial expense. Industries that operate in corrosive environments, such as marine, chemical processing, and transportation, consider galvanized metals indispensable due to the cost savings over a product’s lifecycle.
In terms of technical advantages, the coil galvanizing line ensures a uniform and well-adhered zinc coating, which protects metals not only from surface corrosion but also from crevice and galvanic corrosion through a process known as cathodic protection. This means that even if the coating is scratched, the zinc will corrode preferentially to the base metal, protecting the steel underneath from rusting. Such resilience is critical in extending the functional lifespan of industrial components where safety and reliability are paramount.
To summarize, galvanized metals produced via coil galvanizing lines are integral to multiple industrial applications due to their outstanding corrosion resistance, improved durability, cost effectiveness, and environmental benefits. The coil galvanizing line itself represents a vital technological advancement that allows for precise, efficient, and scalable production of galvanized steel products essential to modern industrial needs.
Conclusion
Certainly! Here’s a well-rounded, engaging conclusion for your article titled **"The Role of Coil Galvanizing Lines in Corrosion Resistance and Metal Durability"**:
---
In conclusion, coil galvanizing lines play a pivotal role in enhancing the corrosion resistance and overall durability of metal products, making them indispensable in today’s industrial landscape. By providing a uniform and robust zinc coating, these lines significantly extend the lifespan of metal components, reducing maintenance costs and environmental waste caused by premature metal failure. From an engineering perspective, the precision and efficiency of modern galvanizing processes ensure consistent quality and performance, meeting the rigorous demands of construction, automotive, and infrastructure sectors. Furthermore, as industries move toward sustainability, coil galvanizing emerges as a cost-effective, eco-friendly solution that preserves natural resources through prolonged metal usage. Ultimately, investing in advanced coil galvanizing technology not only safeguards metal assets but also contributes meaningfully to a resilient and sustainable future.
---
If you’d like the conclusion to emphasize a particular perspective—such as economic benefits, technological advances, environmental impact, or industry applications—just let me know!